Posts Tagged: Real Estate
A Comprehensive Guide to Home Financing Options in Malaysia
Looking to buy a home in Malaysia but feeling overwhelmed by the plethora of financing options available? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the various home financing options in Malaysia, providing you with all the information you need to make an informed decision. From H1 tags to H3 tags, each article is carefully structured to ensure easy navigation and understanding. With a minimum of 2500 words per article, we delve into the world of home financing in a friendly and approachable tone, making it a breeze for you to explore further. So grab a cup of tea, sit back, and let’s dive into the exciting world of home financing options in Malaysia!
A Comprehensive Guide to Home Financing Options in Malaysia
Buying a home is an exciting milestone in your life, but it can also be a complex and overwhelming process. One of the most crucial aspects of purchasing a property is securing the right home financing option. With so many choices available in Malaysia, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the various home financing options before making your decision. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of home loans and financing schemes available to help you make an informed choice.
1. Conventional Home Loans
1.1 Overview of Conventional Home Loans
Conventional home loans are the most common type of financing option in Malaysia. They are offered by banks and financial institutions and are governed by the standard lending practices. Conventional home loans are not linked to any specific religious or cultural requirements and are suitable for individuals of all backgrounds.
1.2 Features and Benefits
Conventional home loans come with several features and benefits that make them a popular choice among homebuyers. These include flexible repayment options, competitive interest rates, and the ability to prepay the loan without incurring any penalties. Additionally, conventional home loans can be used to finance all types of residential properties, such as landed houses, apartments, and condominiums.
1.3 Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for a conventional home loan, you generally need to meet certain criteria set by the lending institution. This includes having a stable source of income, a satisfactory credit history, and a reasonable debt-to-income ratio. The specific eligibility criteria may vary between lenders, so it’s important to check with the chosen institution to ensure you meet their requirements.
1.4 Application Process
When applying for a conventional home loan, you will typically need to provide the lender with various documents, such as proof of identity, income statements, and property details. The application process may involve a thorough assessment of your financial situation, creditworthiness, and the property you intend to purchase. It’s essential to gather all the necessary documents and submit them accurately to expedite the loan approval process.
1.5 Pros and Cons
Like any other financing option, conventional home loans have their advantages and disadvantages. Some of the pros include the flexibility to choose from a wide range of lenders, competitive interest rates, and the potential for higher loan amounts. However, one of the downsides of conventional home loans is that they do not cater to individuals with specific religious requirements. Additionally, the approval process may involve strict eligibility criteria and a longer time frame compared to other financing options.
2. Islamic Home Financing
2.1 Introduction to Islamic Home Financing
Islamic home financing, also known as Shariah-compliant financing, is a type of home loan that adheres to the principles of Islamic finance. It caters to individuals who prefer financing options that align with their religious beliefs. Islamic home financing operates on the concept of profit and risk-sharing, rather than interest-based lending.
2.2 Principles of Islamic Financing
Islamic home financing is guided by principles outlined in Islamic law, known as Shariah. The key principles include the prohibition of charging or receiving interest (riba), the avoidance of uncertainty (gharar), and the prohibition of investment in unethical activities (haram). Instead, Islamic home financing utilizes concepts such as profit-sharing (mudarabah), cost-plus financing (murabahah), and leasing (ijara) to facilitate the purchase of a property.
2.3 Types of Islamic Home Financing
There are different types of Islamic home financing options available in Malaysia, each with its own unique features. Some popular options include Musharakah Mutanaqisah, Ijarah Muntahiyah Bittamlik, and Bay’ Bithaman Ajil. These options offer variations in terms of profit-sharing, ownership structure, and payment methods, allowing borrowers to choose an option that best suits their needs.
2.4 Eligibility and Documentation
The eligibility criteria and documentation requirements for Islamic home financing are similar to conventional home loans. Borrowers need to have a stable income, good credit history, and meet the lender’s specific requirements. In addition, Islamic home financing may require additional documentation related to the specific Islamic finance principles being applied.
2.5 Comparison with Conventional Home Loans
Islamic home financing differs from conventional home loans primarily in the way the loans are structured and the principles they abide by. While conventional home loans charge interest, Islamic home financing uses alternative methods such as profit-sharing or cost-plus financing. Additionally, Islamic home financing caters to individuals with specific religious requirements, providing an alternative for those who want to ensure adherence to Islamic principles.
3. Fixed-Rate Home Loans
3.1 Basics of Fixed-Rate Home Loans
Fixed-rate home loans are a popular choice for individuals seeking stability and predictability in their loan repayments. With a fixed-rate loan, the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan tenure, allowing borrowers to plan their finances with confidence. This is in contrast to variable-rate loans, where the interest rate can fluctuate over time.
3.2 Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the advantages of a fixed-rate home loan is that it provides borrowers with a consistent repayment amount, making it easier to budget and manage finances. It also offers protection against potential interest rate hikes, as borrowers are not affected by market fluctuations. However, the downside of fixed-rate home loans is that they typically come with higher interest rates compared to variable-rate loans. Additionally, borrowers may miss out on potential savings if interest rates decrease during the loan tenure.
3.3 Choosing the Right Terms and Tenure
When opting for a fixed-rate home loan, it’s crucial to carefully consider the loan terms and tenure. The loan term refers to the duration over which the loan will be repaid, while the loan tenure determines the number of years it will take to fully repay the loan. It’s important to strike a balance between a shorter loan term, which may result in higher monthly repayments, and a longer loan term, which may result in higher overall interest payments.
3.4 Application Process
The application process for a fixed-rate home loan is similar to other home loans. Borrowers need to provide the necessary documentation, such as proof of identity, income statements, and property details. Lenders will assess the borrower’s eligibility based on factors such as creditworthiness, debt-to-income ratio, and employment stability. Once approved, the loan agreement will outline the fixed interest rate, loan terms, and repayment schedule.
3.5 Understanding the Loan Repayment
With a fixed-rate home loan, the repayment amount remains consistent throughout the loan tenure. Borrowers make regular monthly payments that include both the principal amount and the fixed interest rate. By understanding the loan repayment structure, borrowers can effectively plan their finances and ensure timely repayment to avoid any penalties or defaults.
4. Variable-Rate Home Loans
4.1 Introduction to Variable-Rate Home Loans
Variable-rate home loans, also known as adjustable-rate mortgages, are loans with interest rates that can change over time. Unlike fixed-rate loans, where the interest rate is locked in for the entire loan tenure, variable-rate loans are subject to market fluctuations and adjustments based on economic factors.
4.2 How the Interest Rates are Determined
The interest rates for variable-rate home loans are typically tied to a benchmark rate, such as the Base Rate (BR) or the Islamic Financing Rate (IFR), set by the respective financial institution. The benchmark rate is influenced by factors such as economic conditions, inflation, and monetary policy. When the benchmark rate changes, the interest rate on the variable-rate home loan will adjust accordingly.
4.3 Pros and Cons
Variable-rate home loans offer several advantages. Initially, the interest rates are typically lower compared to fixed-rate loans, allowing borrowers to enjoy lower monthly repayments. Additionally, if interest rates decrease over time, borrowers may benefit from reduced repayment amounts. However, one of the drawbacks of variable-rate loans is the uncertainty associated with fluctuating interest rates. Borrowers need to be prepared for the possibility of higher repayment amounts if interest rates rise.
4.4 Factors to Consider Before Opting for Variable Rates
Before considering a variable-rate home loan, it’s important to assess your risk tolerance and financial capability to handle potential interest rate fluctuations. Borrowers should analyze market conditions, economic forecasts, and consult with financial advisors to make an informed decision. Understanding the potential impact of interest rate changes on your monthly budget and overall financing can help mitigate any future financial strain.
4.5 Risks and Rewards
Variable-rate home loans carry inherent risks and rewards. The reward lies in the potential for lower initial interest rates and the possibility of saving money if interest rates decrease. However, there is also the risk of higher interest rates, leading to increased monthly repayments. Borrowers need to carefully weigh the risks and rewards, considering their financial goals and the long-term impact of possible interest rate fluctuations on their overall repayment strategy.
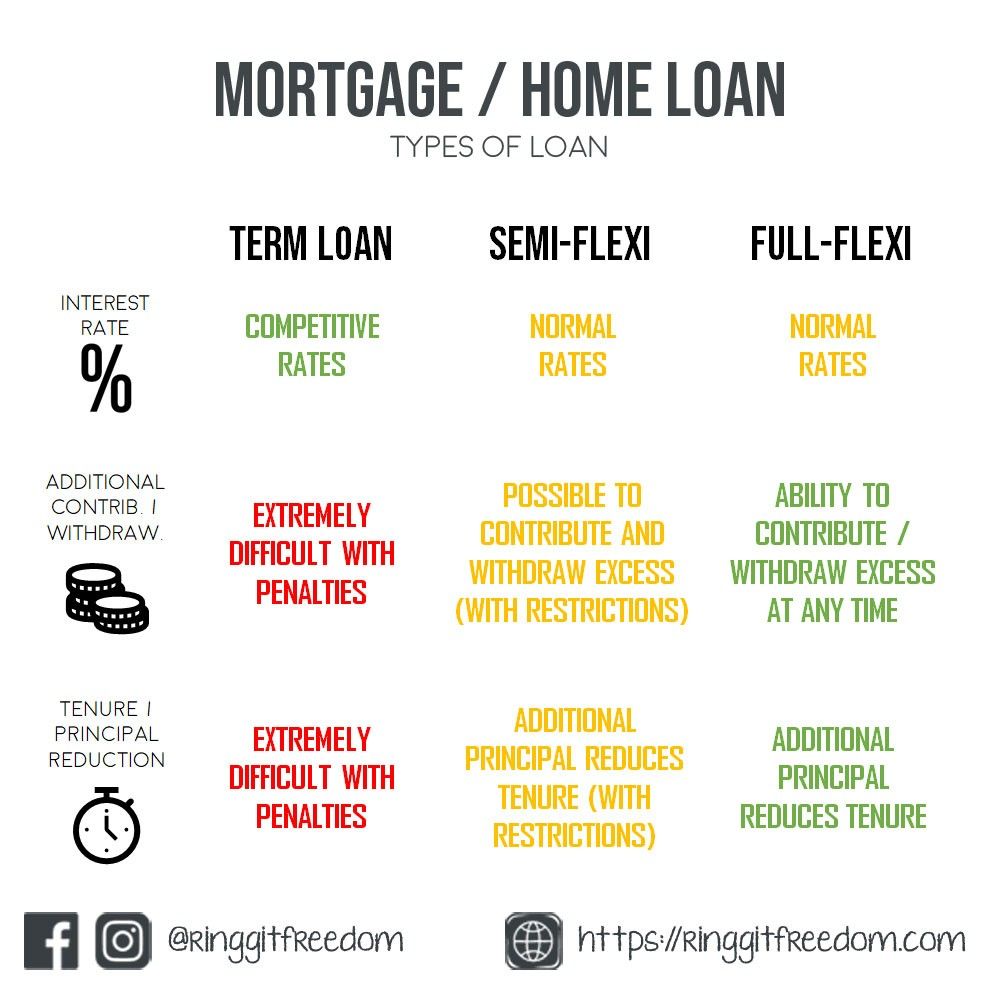
5. Flexi Home Loans
5.1 Understanding Flexi Home Loans
Flexi home loans, also known as flexible home loans, offer borrowers greater control and flexibility over their loan repayments. These loans are designed to provide more options and features that cater to individual financial needs and circumstances.
5.2 Benefits and Features
Flexi home loans offer various benefits and features that make them an attractive option for borrowers. Some of these benefits include the option to make extra repayments, withdraw excess payments, and the potential to reduce the overall interest paid. Flexi home loans also allow borrowers to make changes to their repayment schedules, such as adjusting the loan tenure or taking repayment breaks during emergencies.
5.3 How It Works
Flexi home loans operate on the concept of an overdraft facility linked to the borrower’s home loan account. Any excess funds deposited into the account can be used to offset the outstanding loan amount, effectively reducing the loan tenure and overall interest paid. Borrowers can also withdraw the excess funds if needed, providing a safety net during financial emergencies.
5.4 Eligibility and Considerations
The eligibility criteria for flexi home loans are similar to other home loan options. Borrowers need to meet the lender’s requirements in terms of income, credit history, and property details. It is important to consider factors such as the annual fee, late payment charges, and minimum balance requirements associated with the flexi home loan facility. It’s also essential to evaluate your financial capability to take advantage of the flexibility offered by this loan option effectively.
5.5 Repayment Options and Strategies
With flexi home loans, borrowers have the flexibility to choose from different repayment options and strategies. They can opt for regular monthly repayments or make extra repayments whenever they have surplus funds. The extra repayments can help offset the loan principal and reduce the overall interest paid. Borrowers can also take advantage of features like the redeposit facility, which allows any withdrawn excess funds to be redeposited into the loan account, further reducing the interest payable.
6. Government Home Financing Schemes
6.1 My First Home Scheme
The My First Home Scheme is a government initiative aimed at assisting first-time homebuyers in Malaysia. It is designed to make homeownership more accessible to young individuals or families who have yet to own a property. The scheme offers various benefits such as financing up to 100% of the property value, preferential interest rates, and longer loan tenures.
6.2 PR1MA Home Financing
PR1MA Home Financing is a government initiative managed by PR1MA, the 1Malaysia People’s Housing Programme. The program provides affordable housing options for middle-income individuals and families in Malaysia. PR1MA Home Financing offers attractive financing packages, including high loan-to-value ratios, competitive interest rates, and flexible repayment options.
6.3 First Home Deposit Funding Scheme (MyDeposit)
The First Home Deposit Funding Scheme, also known as MyDeposit, is an initiative aimed at assisting first-time homebuyers in saving for the deposit required to purchase a property. Under the scheme, eligible individuals can receive financial assistance in the form of a 10% deposit, up to a maximum of RM30,000. MyDeposit helps bridge the affordability gap and makes homeownership more attainable for aspiring homeowners.
6.4 Skim Rumah Pertamaku
Skim Rumah Pertamaku, or My First Home Scheme (SRP), is another initiative introduced by the government to assist first-time homebuyers. The scheme offers various incentives and benefits, including higher loan limits, lower interest rates, and partial stamp duty exemptions. The SRP aims to encourage homeownership among first-time buyers and provide them with the necessary financial support to enter the property market.
6.5 Other Government Initiatives
In addition to the aforementioned schemes, there are other government initiatives aimed at promoting homeownership and providing affordable housing options. These include programs such as Rumah Selangorku, Program Perumahan Rakyat, and various state-sponsored affordable housing schemes. Each program has its own eligibility criteria, benefits, and guidelines, catering to different segments of the population based on income levels and geographical locations.
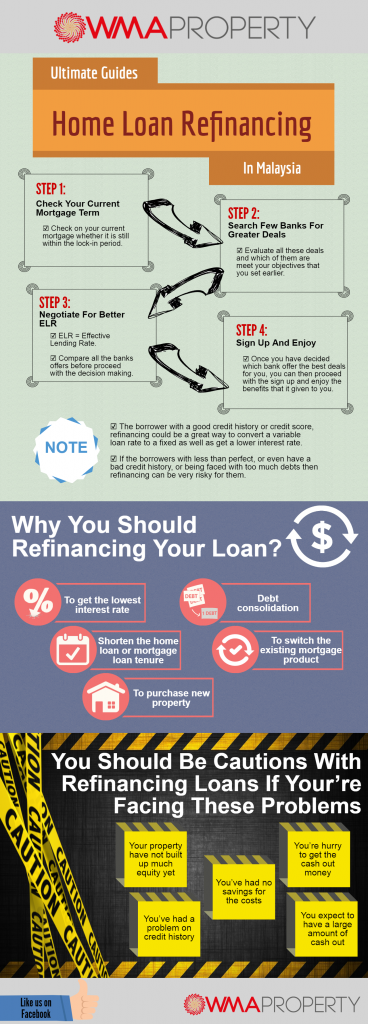
7. Home Loan Refinancing
7.1 Reasons for Refinancing
Home loan refinancing refers to the process of replacing an existing home loan with a new loan from another lender. There are several reasons why borrowers choose to refinance their home loans. These include obtaining a better interest rate, reducing monthly repayments, consolidating debts, accessing additional funds for home improvements, or changing loan tenure to better suit their financial goals.
7.2 When to Refinance
Deciding when to refinance your home loan depends on various factors, such as prevailing interest rates, your financial situation, and the costs associated with refinancing. It’s essential to assess whether refinancing will result in significant savings or benefits that outweigh the costs involved. Refinancing at the right time can potentially help you secure better loan terms and optimize your overall financial position.
7.3 Benefits and Drawbacks
Refinancing a home loan can offer several benefits, including the potential for lower interest rates, reduced monthly repayments, and access to additional funds. It can also help consolidate debts and improve your overall financial management. However, there are also drawbacks to consider, such as upfront costs, potential penalties for early loan repayment, and the impact on your credit score. It’s important to weigh these factors before deciding to refinance.
7.4 The Refinancing Process
The refinancing process involves several steps, including researching and comparing different lenders, gathering the necessary documentation, submitting an application, and undergoing a credit assessment. If approved, the new lender will pay off your existing loan, and you will start making repayments to the new lender under the new loan terms. It’s essential to carefully review the new loan agreement and understand the terms and conditions before finalizing the refinancing process.
7.5 Tips for Successful Refinancing
To ensure a successful refinancing experience, it’s important to follow a few tips. Start by conducting thorough research and comparing various lenders to find the most favorable terms and conditions. Prepare all the necessary documents in advance to streamline the application process. Assess your financial situation and goals to determine if refinancing aligns with your needs. Finally, consult with a financial advisor to fully understand the implications of refinancing and make an informed decision.
8. Home Equity Financing
8.1 Understanding Home Equity
Home equity refers to the portion of your property value that you own outright. It is the difference between the market value of your property and the outstanding amount of your home loan. Home equity increases as you make mortgage repayments and with any appreciation in property value.
8.2 Home Equity Loan vs. Home Equity Line of Credit
Home equity financing, also known as a home equity loan or a home equity line of credit (HELOC), allows homeowners to borrow against the equity in their property. A home equity loan provides a lump sum amount with fixed repayments, while a HELOC offers a revolving line of credit that can be drawn from as needed. Homeowners can choose the option that best suits their financial needs and goals.
8.3 Uses of Home Equity Financing
Home equity financing can be used for various purposes, including home improvements, debt consolidation, education expenses, or emergency funds. The funds obtained through home equity financing can provide homeowners with the flexibility and convenience to access cash when needed, often at lower interest rates compared to other forms of borrowing.
8.4 Eligibility and Application Process
To be eligible for home equity financing, homeowners typically need to have a minimum level of equity built up in their property. Lenders may have specific requirements regarding loan-to-value ratios and creditworthiness. The application process involves submitting the necessary documentation, undergoing a credit assessment, and having the property independently valued to determine the available equity.
8.5 Considerations and Risks
Home equity financing carries certain considerations and risks. Borrowing against your home equity means using your property as collateral, putting it at risk in case of default. It’s crucial to carefully consider the purpose and necessity of borrowing against your home equity and ensure that the repayment terms are manageable within your financial means. Additionally, fluctuations in property value can impact the available equity and borrowing capacity.
9. Bridging Loans
9.1 Overview of Bridging Loans
Bridging loans are short-term financing options designed to help borrowers bridge the financial gap between the purchase of a new property and the sale of their existing property. These loans provide temporary funding to cover the down payment or purchase price of the new property until the proceeds from the sale are received.
9.2 When to Use Bridging Loans
Bridging loans are typically used in situations where the timing of property transactions does not align. For example, if you have found your dream home but have not yet sold your current property, a bridging loan can provide the necessary funds to secure the new property while you wait for the sale proceeds.
9.3 How Bridging Loans Work
Bridging loans work by providing borrowers with short-term financing in the form of a loan secured against the property being purchased. The loan is typically repaid when the proceeds from the sale of the existing property are received. Bridging loans can be structured with several repayment options, such as monthly interest payments or deferred repayment until the sale is finalized.
9.4 Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility for bridging loans is generally based on the value of the existing property, the loan-to-value ratio, and the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. Lenders will also consider factors such as the expected sale price and timeline of the existing property sale. It’s important to note that bridging loans typically have higher interest rates and additional fees compared to traditional home loans.
9.5 Repayment and Risks
Repayment of a bridging loan occurs once the proceeds from the sale of the existing property are received. The loan terms will specify the repayment structure, which may include the payment of interest only during the bridging period or the accumulation of interest that is repaid at the end of the loan term. It’s important to carefully consider the risks associated with bridging loans, such as changes in property market conditions or delays in the sale of the existing property.
10. Construction Loans
10.1 Introduction to Construction Loans
Construction loans are specifically designed to finance the construction or renovation of a property. These loans provide funds in stages to cover the costs associated with the different phases of the construction project. Construction loans are temporary in nature and are generally converted to long-term financing, such as a conventional home loan, once the construction is completed.
10.2 Process and Stages of Construction Loans
Construction loans typically involve a phased release of funds based on the construction progress. The loan disbursement is structured in stages, such as land purchase, foundation, roof completion, and final completion. Each stage requires verification and inspection by the lender to ensure that the construction is progressing as planned. The funds are released to the borrower or directly to the contractor based on the completion of each stage.
10.3 Loan Disbursement Methods
The disbursement of funds in construction loans can be managed in different ways. One method involves the lender directly making payments to the contractor or suppliers based on invoices and receipts. Another method, known as the reimbursement method, requires the borrower to make the payments and submit reimbursement requests to the lender for approved amounts. The chosen method will depend on the agreement between the lender, borrower, and contractor.
10.4 Eligibility and Documentation
Eligibility for construction loans is based on factors such as the borrower’s financial capability, creditworthiness, and the feasibility of the construction project. Lenders will typically require a detailed construction plan, cost estimates, and the necessary permits or approvals. Providing accurate and comprehensive documentation is essential to facilitate the loan approval process and ensure smooth disbursement of funds.
10.5 Managing Construction Loan Risks
Construction loans come with inherent risks that borrowers need to be aware of. These risks can include cost overruns, delays in construction, or failure to complete the project. It’s important to work with reputable contractors, obtain all necessary permits, and have contingency plans to address any unforeseen challenges. Regular communication with the lender and proactive management of the construction project can help mitigate risks and ensure a successful outcome.
In conclusion, choosing the right home financing option is a crucial decision that can impact your financial well-being for years to come. It’s important to explore and understand the various options available in Malaysia, considering factors such as your financial situation, long-term goals, and specific requirements. By being well-informed and seeking professional advice when needed, you can navigate the home financing landscape with confidence and make an informed decision that suits your needs and aspirations.
